Encrypted DNS, Episode II
Carsten Strotmann, Men & Mice
August 2020
Created: 2020-08-19 Wed 09:05
Agenda
- DNS-Privacy
- DoH/DoT/DoQ
- The current status
- Oblivious DoH and Adaptive DNS resolver discovery
About me?
Carsten Strotmann
~ 20 years with Men & Mice
DNS(SEC)/DANE/DHCP/IPv6 trainer and supporter
RIPE/IETF
Privacy in DNS?
- in recent years, the IETF has expanded the DNS protocol with privacy features
- DNS-over-TLS (Transport-Encryption between DNS client and DNS resolver)
- DNS-over-HTTPS (Transport-Encryption between DNS client and DNS resolver)
- QNAME Minimization (less metadata in DNS)
- EDNS-Padding (hiding of DNS data in encrypted connections)
The need for more DNS privacy
- a study presented at IETF 105 during the Applied Networking Research Workshop in July 2019 found that
- 8.5 % of networks (AS) intercept DNS queries (27.9% in China)
- (today) most queries are answered un-altered
- but the situation might change, intercept server might change DNS answers
encrypted transport for DNS
encrypted DNS terminology
- Terminology
Do53= DNS-over-Port53 - classic DNS (UDP/TCP port 53)DoT= DNS-over-TLS - TLS as the transport for DNSDoH= DNS-over-HTTPS - HTTPS as the transport for DNSDoQ= DNS-over-QUIC - QUIC as the transport for DNSDoC= DNS-over-Cloud - DNS resolution via cloud services (Google, Q9, Cloudflare …)
DoT - DNS-over-TLS
- RFC 7858 "Specification for DNS over Transport Layer Security (TLS)"
- DNS wireformat over TLS over TCP
- Port 853 (TCP)
- Encryption and Authentication (Internet PKI or via DANE)
DoH - DNS over HTTP(S)
- RFC 8484 DNS Queries over HTTPS (DoH) (P. Hoffman, ICANN and P. McManus, Mozilla) https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8484
- DNS HTTP-Format over HTTPS over TCP, Port 443 (HTTP/2)
- URL: https://server/dns-query{?dns}"
- Encryption, Authentication and Cloaking
DoH timeline
- IETF 100 - November 2017 - DNS over HTTP(S) (DoH) workinggroup started: https://datatracker.ietf.org/wg/doh/about/
- IETF 101 - March 2018 - work on DNS Queries over HTTPS finished, start of working group last call (WGLC) in April 2018
- October 2018 - RFC 8484 published
DNS-over-HTTPS and IDS/Network-filter
Quote from RFC 8484:
Operational Considerations […] Filtering or inspection systems that rely on unsecured transport of DNS will not function in a DNS over HTTPS environment due to the confidentiality and integrity protection provided by TLS.
DoT vs DoH
- differences between DoT and DoH
- DoT can be easily blocked, because it is running on an dedicated port (853)
- DoH is made to look like normal HTTPS traffic, selective blocking of DoH is difficult
- DoH seems to be easier to implement, because of existing HTTPS library functions in programming languages
- DoH enables developers to do DNS name resolution on an application level, which some people think is bad
The DoH dilemma
- to reach the Internet users that are in need of privacy, DoH needs
to be enabled by default
- DoH Server selection can be seen as similar to the CA selection browsers do
- a fixed selection "per region" will (still) lead to centralization
of all DNS queries with a few DNS operators
- but that might still be the case even without DoH, some countries in Asia send > 90% of DNS queries to DoC (Google)
- the IETF is working on new protocol specifications to allow clients to discover secure and trusted DNS resolver (ADD "Adaptive DNS Discovery" Working Group)
Controlling DoH - the Canary Domain
Controlling DoH - the Canary Domain
- Mozilla has implemented a check for a Canary Domain in Firefox
- Domain Name
use-application-dns.net.- if the domain-name can be resolved via DNS53 -> unmanaged DNS, DoH can be auto-enabled
- if the domain-name cannot be resolved (= is blocked) -> managed DNS, DoH will not be auto-enabled (but users can manually enable DoH)
- the IETF is discussing similar signalling functions: "Signaling resolver's filtering policies" (draft-mglt-add-signaling-filtering-policies)
other checks done by Firefox before enabling DoH
- Resolve canary domains of certain known DNS providers to detect content filtering
- Resolve the safe-search variants of
google.comandyoutube.comto determine if the network redirects to them - On Windows and macOS, detect parental controls enabled in the operating system
- additional checks performed for private enterprise networks are:
- Is the Firefox
security.enterprise_roots.enabledpreference set to true? - Is any enterprise policy configured?
- Is the Firefox
Current DoT/DoH status
Firefox Browser
- Firefox Trusted Recursive/Remote Resolver (TRR) Program
- Cloudflare (default) or NextDNS
- Comcast XFinity (coming)
- automatic rollout started in February 2020
Chrome(ium) Browser
- DoH is implemented and can be enabled by the user
- Google Chrome
- Opera
- Vivaldi
- Brave
- Microsoft Edge
- Bromite
- DoH "auto upgrade" for the configured DNS resolvers (manual configured or DHCP/RA supplied)
- Google is experimenting with adaptive DoH-Resolver-Discovery via DNS
Safari Browser (iOS, iPadOS, MacOS)
- support for DoH and DoT is coming with iOS 14 and MacOS 11 'Big Sur'
- possibly also support for Adaptive DNS resolver discovery
Microsoft Windows 10 (1/2)
- support in latest "Insider" builds of Windows 10
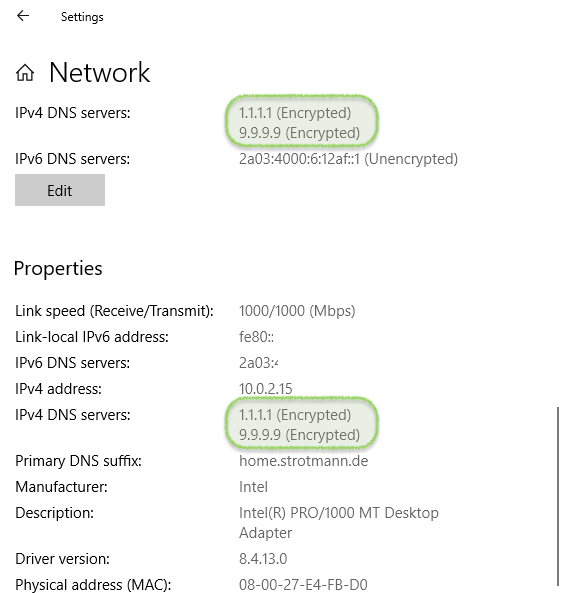
Microsoft Windows 10 (2/2)
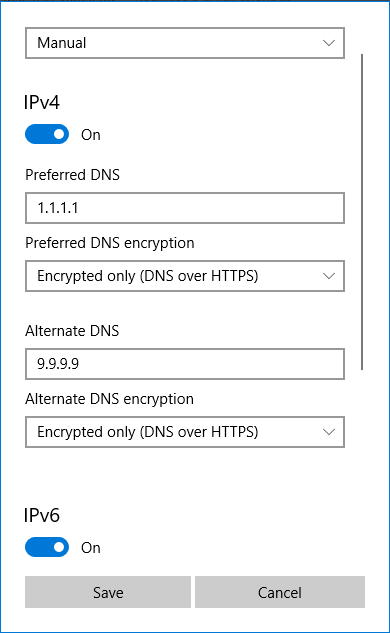
Linux
- DoT support in
systemd-resolvedfor some time - opportunistic mode only (automatic fallback to DNS53)
- no server authentication (MITM possible)
- global or "per interface" setting
- not enabled by default
OpenBSD
- DoT support in
unwind - not enabled by default
- opportunistic "auto update" mode or manual configured "strict" mode
- server authentication via TLS certificate
Android
- DoT available from Andoid 9 "Pie"
- manual setting
- "auto upgrade" from the configured DNS resolver, or Google DNS as fallback
Apple MacOS 11 and iOS/iPadOS 14
- support for DoT and DoH
- global and per App/Application resolver selection possible
- "encrypted DNS" configuration Apps possible, user can choose provider by installing App
- OS can learn "per Domain" DoH/DoT setting via DNS or HTTP (Adaptive DNS-over-HTTPS)
- OS can discover DoH/DoT Server via DHCP/PvD (Provisioning Domains)
or queries to
resolver.arpavia classic DNS53 - Discovery methods in active discussion in the IETF ADD working group
Adaptive DNS-over-HTTPS
Adaptive DNS-over-HTTPS
- Goals (directly taken from the Internet Draft):
- No party other than the client and server can learn or control the names being queried by the client or the answers being returned by the server.
- Only a designated DNS resolver associated with the deployment that is also hosting content will be able to read both the client IP address and queried names for Privacy-Sensitive Connections.
- Clients will be able to comply with policies required by VPNs and local networks that are authoritative for private domains
Designated DoH server for domains
- DoH Servers for a domain can be learned
- from DNSSEC secured HTTPSSVC/SVCB records
- HTTP(S)
ALT-SVCheader - DoH-Server "well-known" URL
- local provisioning domain (PvD)
HTTPSSVC Record
- eliminates additional roundtrip (DNS or HTTP)
- HTTPSSVC provides
- address information (
ipv4hint,ipv6hint) - protocol information (protocol upgrade request -> HTTP/3[QUIC])
- public keys (encrypted client hello)
- other data, such as encrypted DNS resolver hint (
dohuri)
- address information (
HTTPSSVC Example
example.com. IN HTTPSSVC 0 svc.example.net. svc.example.net. IN HTTPSSVC 2 svc1.example.net. ( dohuri=https://doh.example.net/dns-query odohkey="..." )
Oblivious DoH (oDoH)
- oDoH is an extension to DoH that allows client IP addresses to be disassociated from queries via proxying (pauly-dprive-oblivious-doh)
Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH
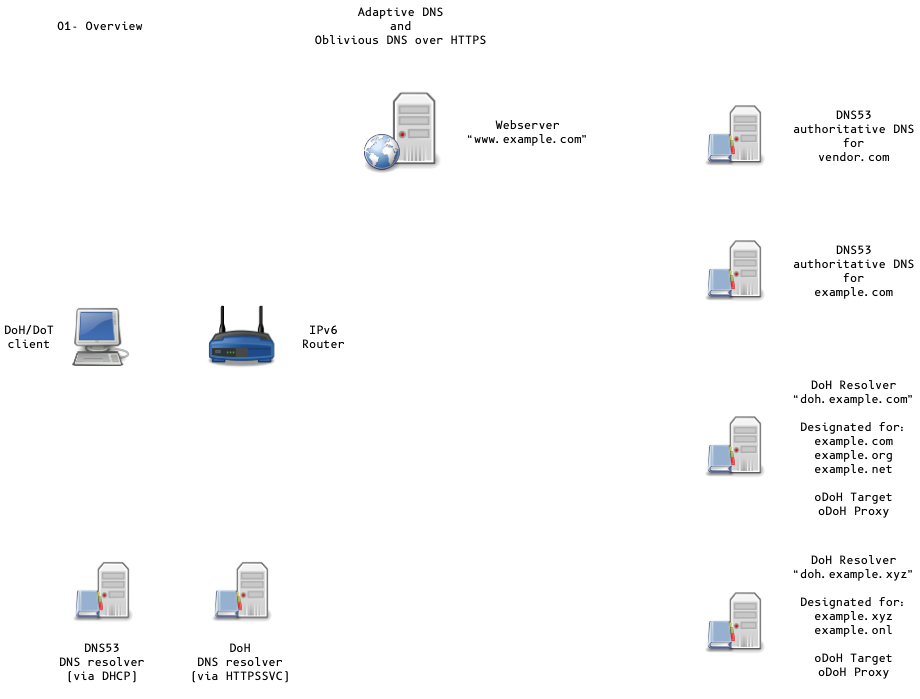
Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH
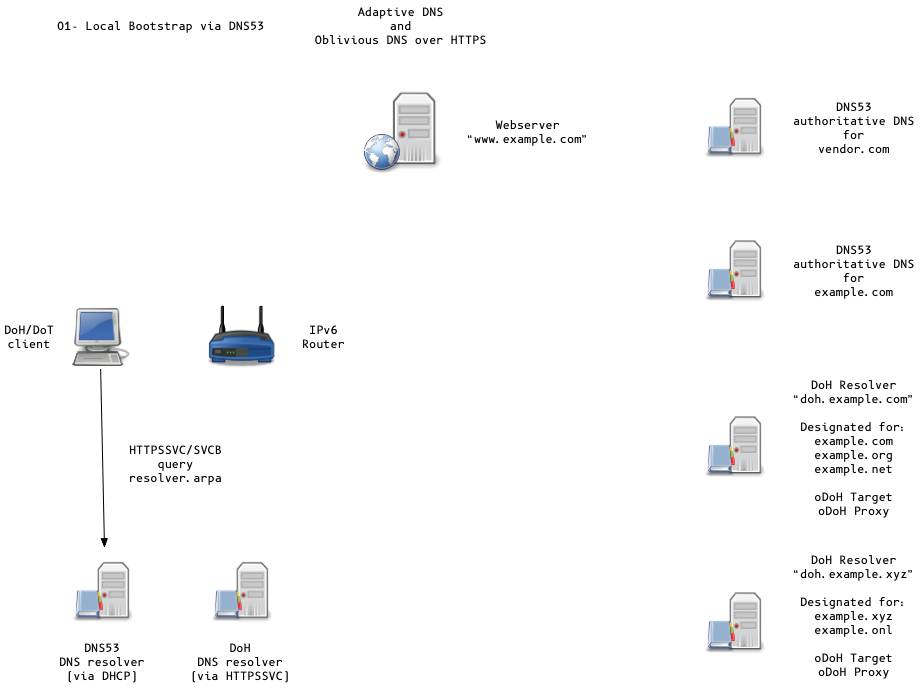
Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH
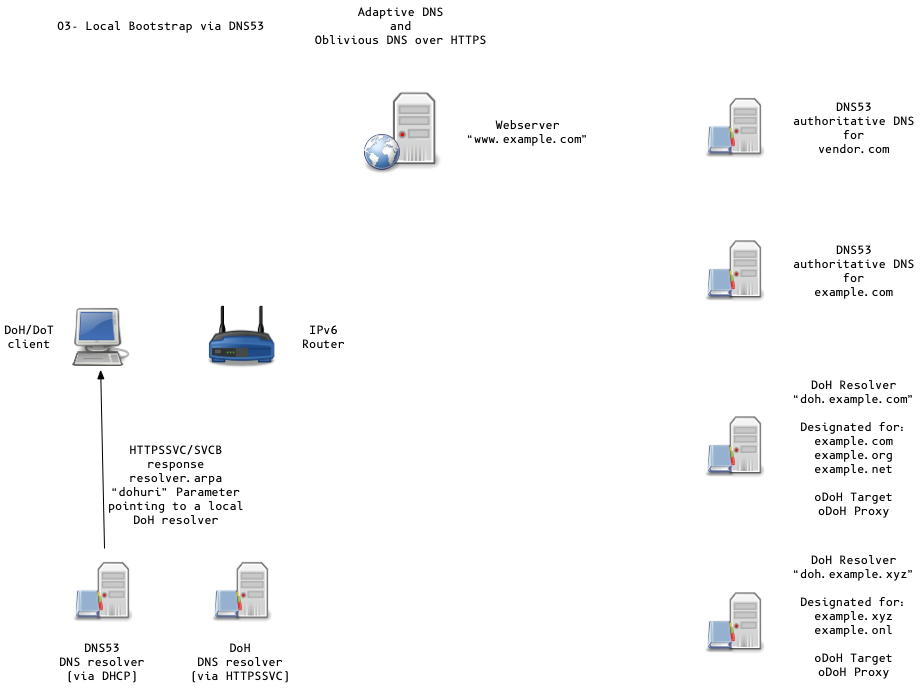
Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH
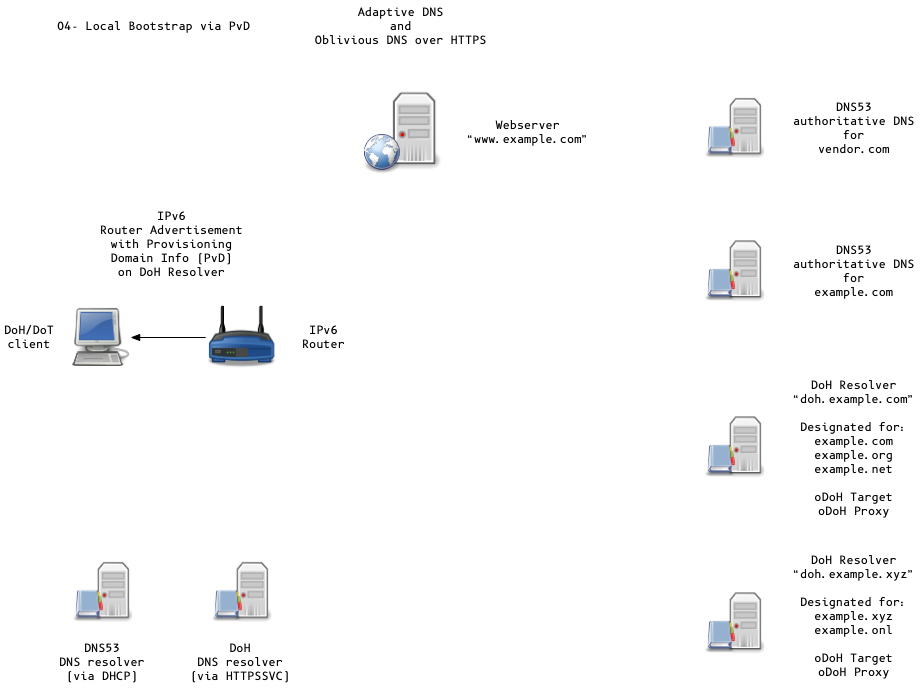
Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH
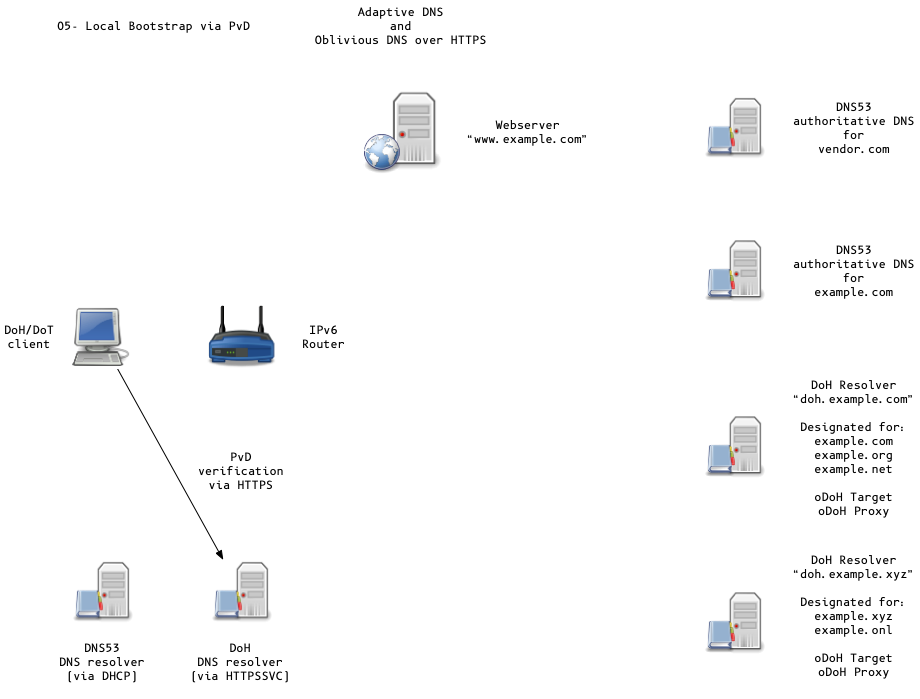
Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH

Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH

Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH

Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH

Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH
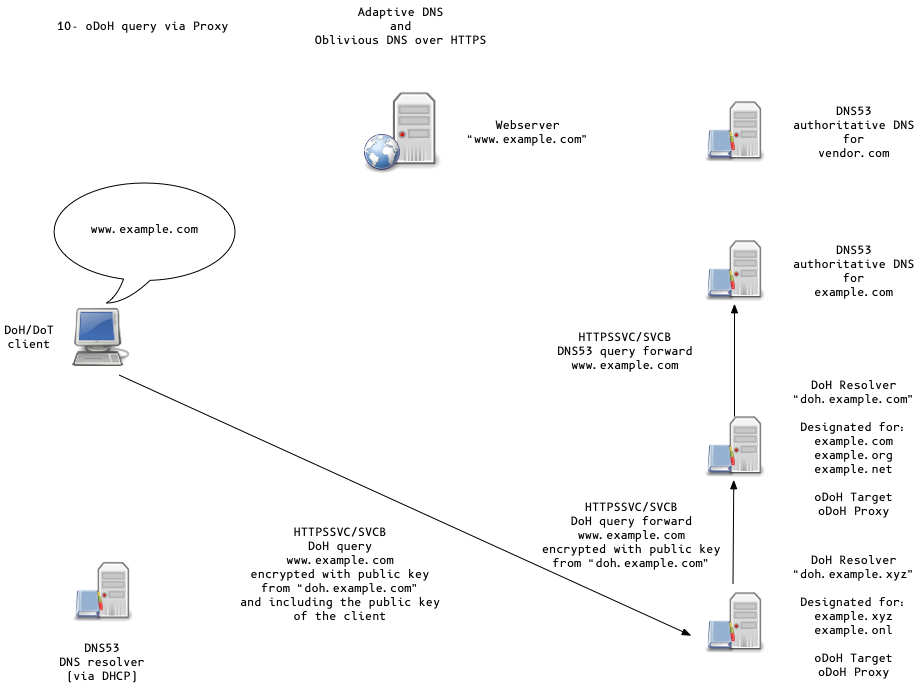
Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH
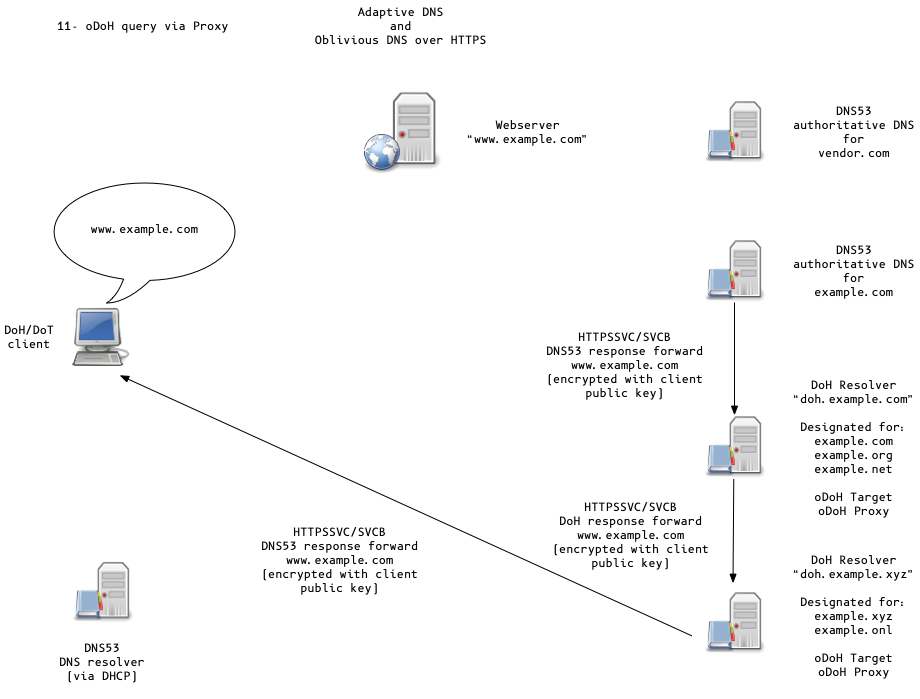
Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH
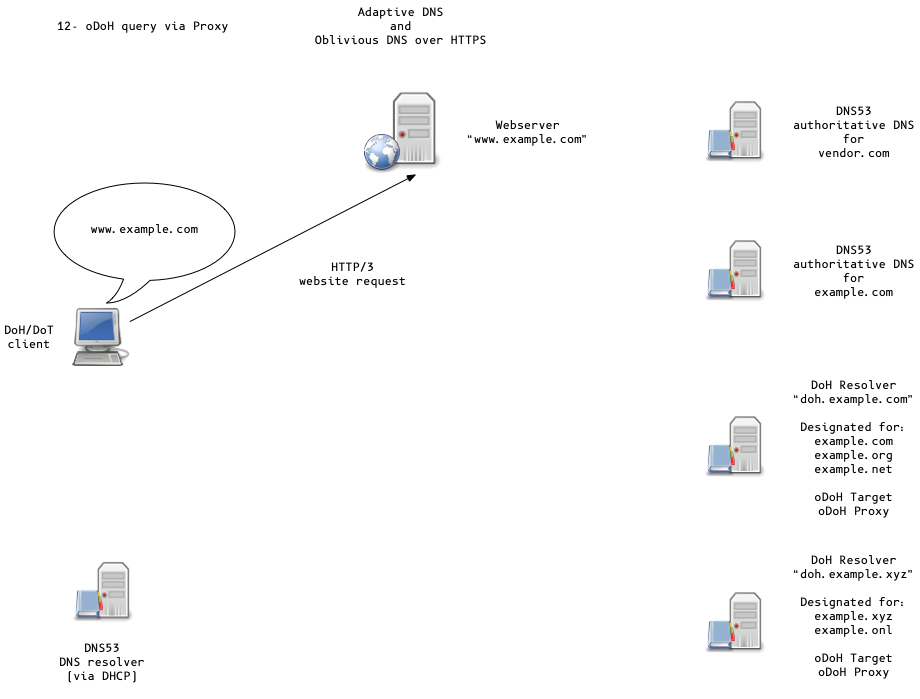
Adaptive DNS Discovery and oDoH
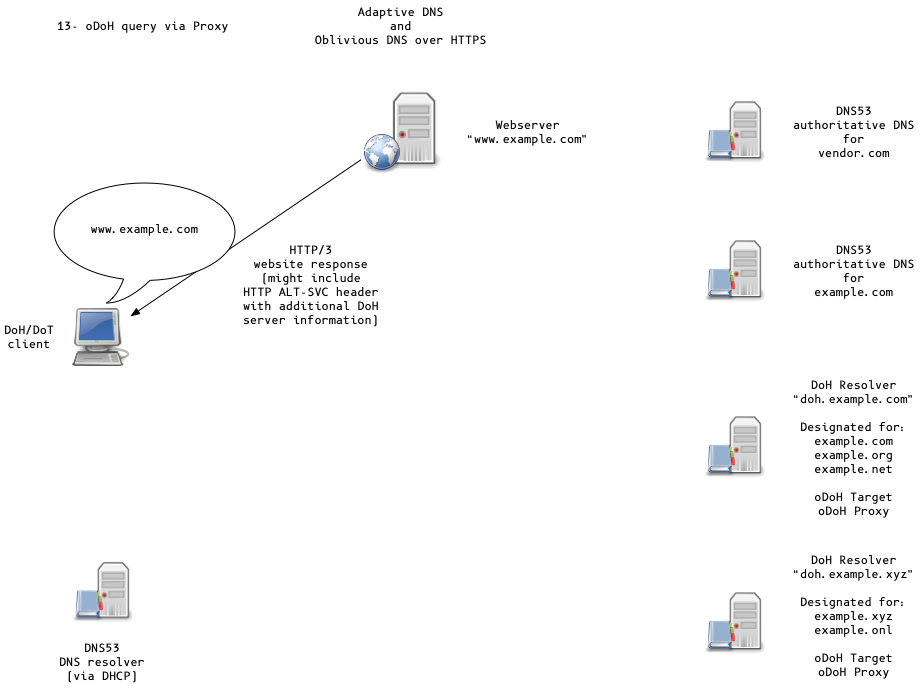
Thank you
Questions
Contact: carsten@menandmice.training